Jaundice management on the postnatal wards
exp date isn't null, but text field is
NICE guidance from 2010 recommends that visual estimation of the severity of neonatal jaundice is no longer used as it is highly inaccurate. The absence of symptoms (i.e. “alert and feeding well”) is not a reliable indicator that treatment is not required either.
Instead whenever neonatal jaundice is seen, the serum bilirubin level should be estimated using transcutaneous bilirubinometry or measured with a blood sample.
This guideline describes the agreed process for the use of transcutaneous bilirubinometers in the post natal wards, and should be used in conjunction with the West of Scotland Neonatal MCN Jaundice guideline. Staff using this access should ensure that they have access to the appropriate gestation specific charts (see appendix), and should refer to them with all results.
Jaundice can develop at any time over the first few days of life. All possible opportunities should be used to look for jaundice over this time.
Assess for jaundice at every interaction with a newborn baby in the first days of life. Ensure adequate lighting. Document the absence or presence of jaundice whenever writing a clinical note. In the “colour” section of the daily check in the SWHMR the presence or absence of jaundice should be noted each day.
Particular attention must be paid to the following groups:
- gestational age under 38 weeks
- a previous sibling with neonatal jaundice requiring phototherapy
- mother's intention to breastfeed exclusively
- visible jaundice in the first 24 hours of life.
Presence of these risk factors should be noted on admission to the ward and it should be ensured that they are regularly assessed for jaundice. NICE recommend that babies with the above factors associated with an increased likelihood of developing significant hyperbilirubinaemia receive an additional visual inspection by a healthcare professional during the first 48 hours of life.
All staff using a transcutaneous bilirubinometer should ensure that they have received adequate training in the use of the device that they have been provided with. Video instructions on the use of devices in circulation can be found here.
- Bilirubin level estimation in all visibly jaundiced neonates in the first 14 days of life
(Except in the following circumstances where serum bilirubins should be measured:
- Less than 24 hours of age (SBR required, see guideline)
- Less than 35 weeks gestation
- Previous phototherapy use)
Caution should also be used where there is known or suspected haemolysis (e.g. where there are maternal blood group antibodies of concern, a history of siblings with severe early haemolysis or the baby is DAT positive in keeping with haemolysis). In this group it may be prudent to use serum bilirubin measurements, at least initially. Any baby falling into this group (known or suspected haemolysis) should have their initial management in a hospital setting and a clear plan for follow up sampling etc made by the discharging paediatrician
Babies over 14 days of age who are visibly jaundiced should follow guidance for prolonged jaundice.
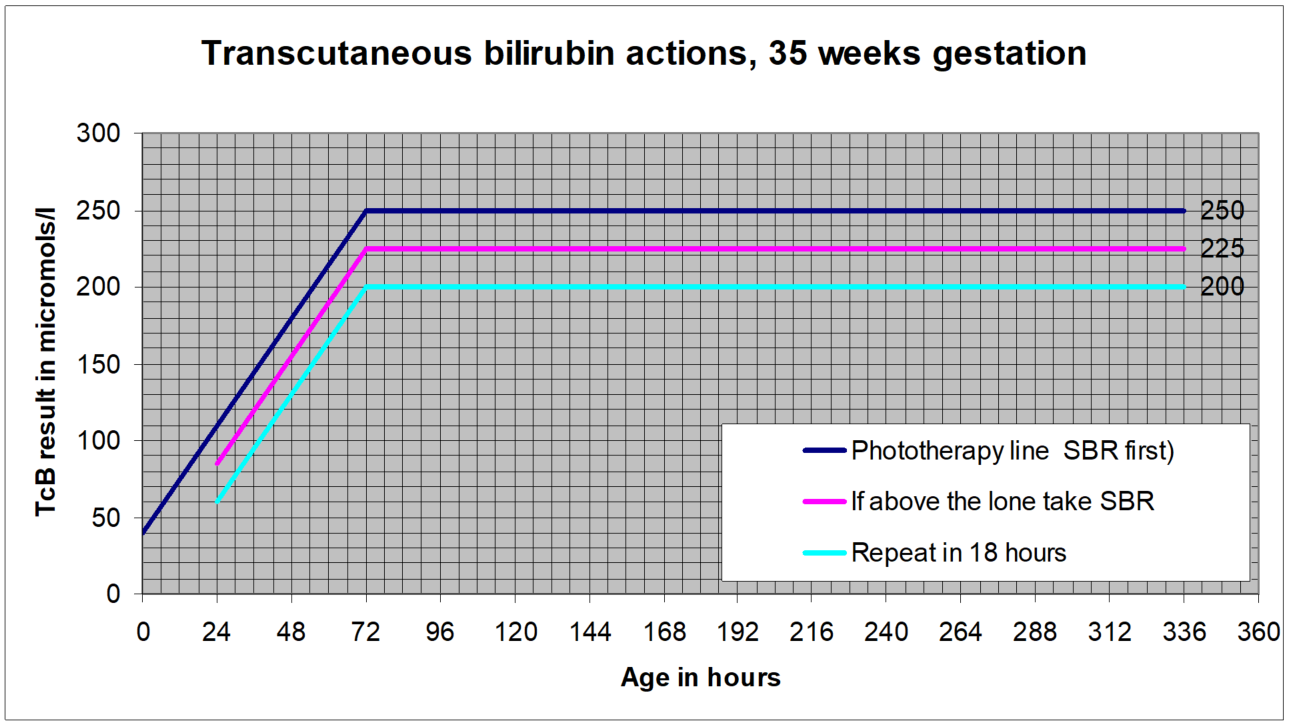
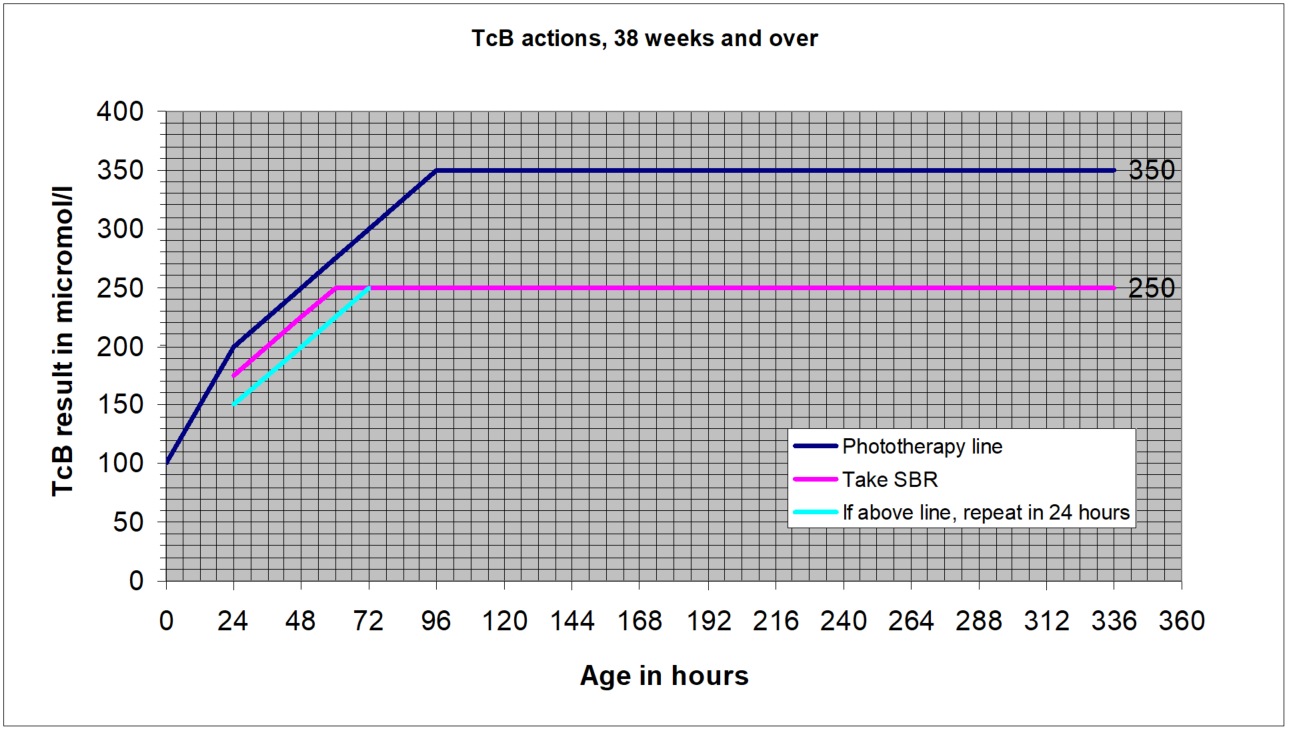
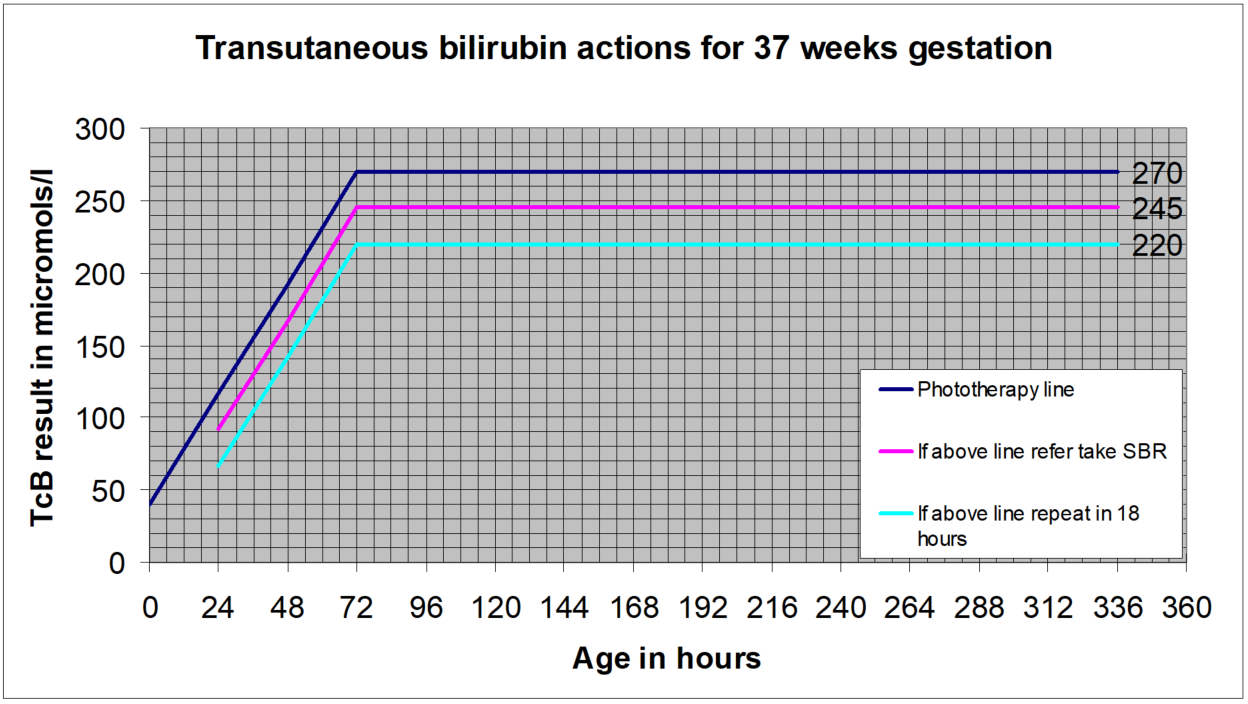
NICE guidance is that for levels up to 250micromol/l transcutaneous measurements are sufficiently accurate to be plotted and acted on without a confirmatory serum bilirubin. Local experience however is less positive than that and so pending further evaluation a “safety margin” will remain in GG&C for more vulnerable infants (less than full term), and for full term infants during the higher risk early days when the bilirubin level is still rising. This margin is that transcutaneous results within 25microl/l of the treatment line should be confirmed with a serum sample. The charts below illustrate this.
A repeat measurement is recommended for those with a level within 50micromol/l of the treatment threshold, as follows:
- Within 24 hours for those at standard risk
- Within 18 hours for those at increased risk:
- Exclusively breast fed
- A sibling who required phototherapy
- Less than 38 weeks gestation
- This may be a challenge in the community setting and a pragmatic approach must be taken for babies who are due to be discharged, e.g. ensure seen as early as possible the following day if the 18 hour recommendation cannot be achieved. Consideration should be given to taking a serum sample in this situation as well to aid decision making.
For all levels, comparison with previous measurements where available is much more informative than looking at a single measurement. This should be borne in mind when using any of these thresholds. Where the rate of rise can be determined it should be used to plan future measurements/samples rather than the action points below. This is particularly relevant on the flatter “plateau” phase of the charts (from 72 or 96 hours of age). If in doubt, please contact neonatal staff.
SBR greater than 50micromol/l below the treatment threshold- no routine repeat required.
- A repeat can be done at any time thereafter if there are clinical concerns or if the rate of rise is a concern. A transcutaneous measurement may be taken to guide whether a further serum sample is required.
SBR within 50micromol/l of the treatment line:
- For standard risk babies: repeat within 24 hours
- For higher risk babies- <38 weeks or exclusively breast fed or with a sibling who required phototherapy: repeat within 18 hours
- This may be a challenge in the community setting and a pragmatic approach must be taken, e.g. ensure seen as early as possible the following day if the 18 hour recommendation cannot be achieved. Liaison with neonatal medical staff/ANNPs may be required in these circumstances.
Process:
For all visibly jaundiced babies (greater than 24 hours, greater than 35 weeks and without previous phototherapy):
- Take a measurement with the transcutaneous bilirubinometer
- Plot the result on the gestation specific charts below
If this is the first measurement act according to the guidance given based on the line immediately below the potted point:
 |
(top line)- treatment threshold (refer) |
| (second line)- take SBR | |
| (third line)- recheck in 18-24 hours. |
If previous measurements are available, decisions around the need for SBR sampling/referral to hospital will depend on whether the level is rising or falling, and the age of the child.
- All rising levels should be considered for a repeat in 24 hours as a minimum, or SBR check depending on their place on the chart
- Stable/falling levels can be assessed and the need for SBR/repeat etc will depend on the age of the child and gestation. In other words, if the transcutaneous level is clearly falling but remains within the “take SBR” zone, an SBR need not necessarily be performed, if previous SBRs have been adequately far from the treatment line.
Stop phototherapy once serum bilirubin has fallen to a level at least 50 micromol/litre below the phototherapy threshold (see treatment threshold graphs).
Check for rebound of significant hyperbilirubinaemia with a repeat serum bilirubin measurement 12–18 hours after stopping phototherapy. Babies do not necessarily have to remain in hospital for this to be done, but a clear plan will need to be made for this to happen, including where appropriate communication with the community midwifery team.
- Transcutaneous billirubin actions, 38 weeks and over
- Transcutaneous billirubin actions for 37 weeks gestation
- Transcutaneous billirubin actions, 36 weeks gestation
- Transcutaneous billirubin actions, 35 weeks gestation
Transcutaneous billirubin actions, 38 weeks and over
Transcutaneous billirubin actions for 37 weeks gestation
Last reviewed: 13 December 2021
Next review: 01 December 2022
Author(s): Dr Allan Jackson – Neonatal Consultant PRM
Co-Author(s): Other Professionals Consulted: Veronica McArthur – Community Midwife PRM
Approved By: GGC Neonatal Guidelines Group